|
Geodetic observatory Pecný
|
|
G-Nut/Anubis - summary output
First line of the Anubis report shows applied version of the software, compilation time and SVN revision number.
Summary section of the Anubis report suggest a low or high verbosity. If sec_sum="1" is used, an overall single-line summary is provided for each GNSS constellation (see listing below).
Description of columns in overall summary (extended teqc single-line) is following:
- Hours_ - data length in hours (estimated from total number of epochs and sampling rate)
- Sample - data sampling interval (estimated from elevation histogram)
- MinEle - data minimum elevation angle observed
- #_Expt - number of expected observations above the horizon (carrier phases with maximum observations over GNSS counted)
- #_Have - number of existing observations above the horizon (carrier phases with maximum observations over GNSS counted)
- %Ratio - ratio of existing and expected observations above the horizon (calculated form above values)
- o/slps - number of observations per cycle slip
- woElev - number of observations with available elevation (no satellite position available)
- Expt>10 - number of expected observations above user mask (carrier phases with maximum observations over GNSS counted)
- Have>10 - number of existing observations above user mask (carrier phases with maximum observations over GNSS counted)
- %Rt>10 - ratio of existing and expected observations above user mask (calculated form above values)
Description of columns in GNSS-specific summary is following:
- ExpEp - number of expected epochs (uses pre-defined data interval and sampling or suggests from data if not available)
- HavEp - number of available epochs (really counted epochs)
- UseEp - number of usable epochs (criterion is 4 satellites in the epoch with dual-frequency data in each GNSS constellation)
- xCoEp - number of epochs with less than 4 satellites providing dual-frequency pseudorange observations
- xPhEp - number of epochs with less than 4 satellites providing dual-frequency carrier-phase observations
- xCoSv - number of single-frequency pseudorange data only
- xPhSv - number of single-frequency carrier-phase data only
- csTot - number of total phase cycle-slips or interruptions (in general means request to setup a new initial phase ambiguity
- csEpo - number of interruptions due to missing epoch (counts all previously observed satellite)
- csSat - number of interruptions due to missing satellite at a specific epoch (where it is expected)
- csSig - number of interruptions due to missing signal from the satellite (others are available)
- nSlp - number of identified phase cycle-slips when continuous tracking is available for specific satellite and signal
- nJmp - number of identified receiver clock jumps
- nGap - number of data total gaps (according to the setting int_gap="600" in seconds)
- nPcs - number of small data pieces (according to the setting int_pcs="1800" in seconds)
- mpX - code multipath moving average RMS [cm] for the 1st..8th band, (mean value over all available signals at the 1st..8th band)

High verbosity provides results of statistics of individual observation types of all available GNSS constellations (see listing below). The following columns are available with/without navigation messages:
- nSat - number of observed satellites
- ExpObs - number of expected observations (an estimate)
- obs[%] - existing observations w.r.t. to expected
- nor[%] - existing observations w.r.t. to expected, but normalized with rate of existing satellites vs. total expected in the constellation
- CS_Tot - number of total phase cycle-slips and phase interruptions
- CS_Epo - number of carrier-phase interruptions due to missing epoch (counted for all previously observed satellites and signals)
- CS_Sat - number of carrier-phase interruptions due to temporary unavailable satellites
- CS_Sig - number of carrier-phase interruptions due to temporary unavailable signals
- CSlips - number of identified real phase cycle-slips in a continuous phase tracking
If navigation messages for specific constellations are available (over the whole QC period!), all intervals of individual satellite visibility can be theoretically calculated and expected observations estimated. Histograms of observations available in columns 0[%] and 0-10, 10-20, .., 80-90 elevations are additionally provided. However, these are actually time-consuming procedures and rather tricky if not all relevant navigation messages are available. Thus the features are supported only experimentally with an extra high verbosity via setting sec_sum="9".

G-Nut/Anubis - configuration
Anubis can be started using a configuration file (or standard input) in XML format. The following forms are equivalent:
The basic command-line help can be get using 'anubis -h' and the example (default) configuration can be received via command 'anubis -X'.
The configuration file consists of main element config (not order required) which contains several sub-elements for specific configurations:
- gen - general settings (interval, constellations, sampling, sites/receivers),
- gnss - GNSS-specific settings (optional to filter out satellites, observation types/bands/attributes, see RINEX3),
- qc - quality check settings (verbosity for all sections, specific settings),
- inputs input files (RINEX navigation and observation files),
- outputs output files (log, QC extraction and, optionally merged RINEX3 navigation).
Supported GNSS constellations and their augmentations are defined via 3-char abbreviations as follows: GPS NAVSTAR (GPS), GLONASS (GLO), Galileo (GAL), BeiDou (BDS), SBAS (SBS), QZSS (QZS). The example Anubis configuration is following:
G-Nut/Anubis - standard point positioning
If reliable navigation messages are available for any global constellation, Anubis estimates coordinates of the receiver using the standard point positioning (SPP) method and pseudo-range observations only. The receiver position is currently estimated for each GNSS separately using a common sampling rate of 15 minutes. Below figures show a) left: the comparison of RMS of NEU coordinate repeatability (expressed in meters) from individual available GNSS and b) right: horizontal epoch-wise positioning with a relative size of point calculated from the Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP) values.


Setting sec_est="1" requests the output of mean coordinates and root-mean-squares calculated from coordinate repeatabilities. Individually, Cartesian and spherical coordinates are reported, while for the latter root-mean-squares are expressed in North,East,Up [m]. Finally, numbers of epochs of all observations and epoch of outliers are reported.
Setting sec_est="2" enables epoch-wise estimates reported in Cartesian and spherical coordinates and the GDOP.
G-Nut/Anubis's gallery
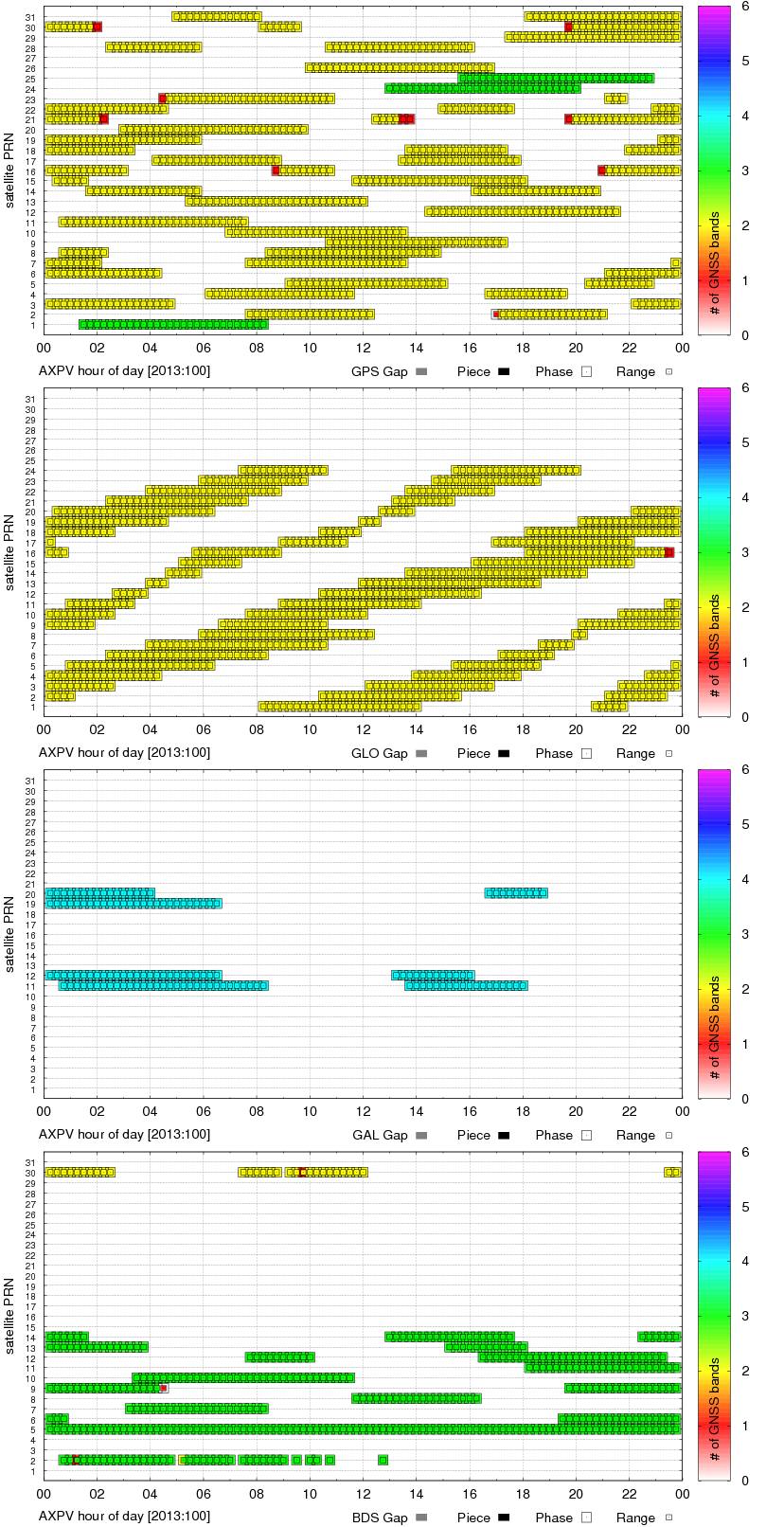
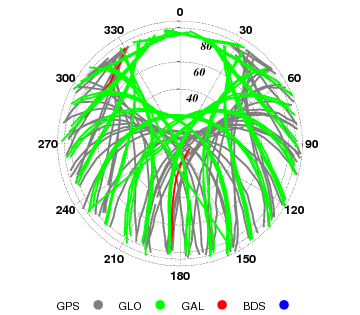
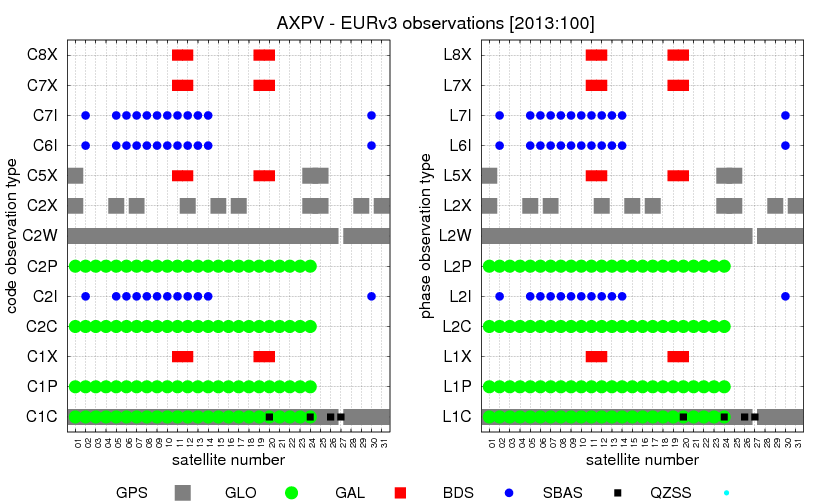
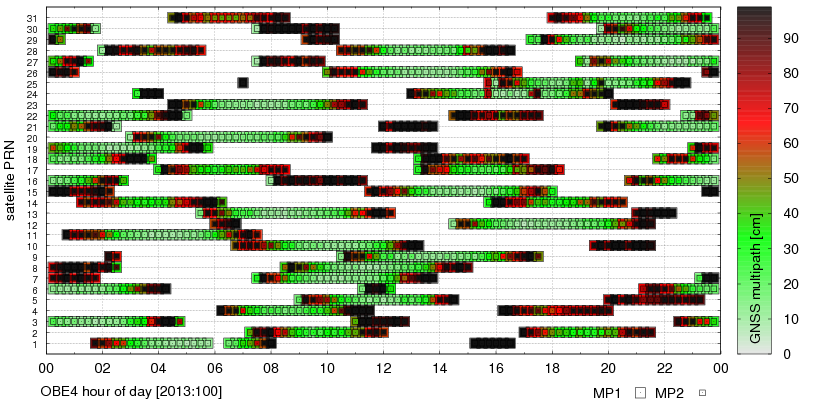
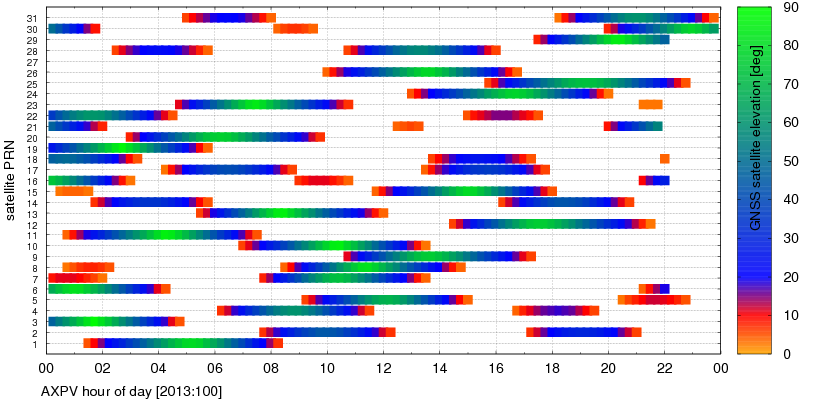

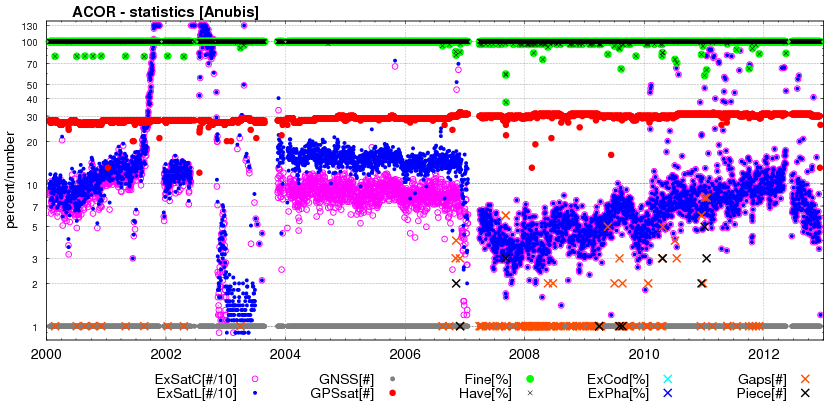
G-Nut/Anubis - code multipath statistics
Code multipath statistics are calculated for all pseudo-range codes of all GNSS satellites providing dual-frequency carrier-phase observations. The statistics are represented as the average RMS of code multipath in [cm] calculated after removing a systematic error from the multipath linear combination. Number of epoch used for estimating the systematic error is set via mpx_nep="15". Detection of discontinuities in the multipath linear combination is controlled by a multiplier of sigma (mpx_lim="3"). The configuration sec_mpx="1" sets a low verbosity while sec_mpx="2" provides time- or elevation-dependent estimates.
The first verbosity (list below right & figure below left) show mean code multipath RMSs
for available signals and all satellites and elevations.

The second verbosity (list below left & figure below right) show the time- and elevation-dependent code multipath estimates.
